Polybutylene Succinate (PBS): Properties, Applications, and Market Prospects
Products & Tech
Feb 10, 2025
781
1. What is Polybutylene Succinate (PBS)?
Polybutylene Succinate (PBS) is a biodegradable polyester, a renewable resource material, which may also be called GsPLA or BioPBS (Mitsubishi Chemical's brand name).
The chemical structure of PBS makes it occupy an important position in the field of environmentally friendly materials. Its main applications cover packaging materials, agricultural films, textiles and other fields.
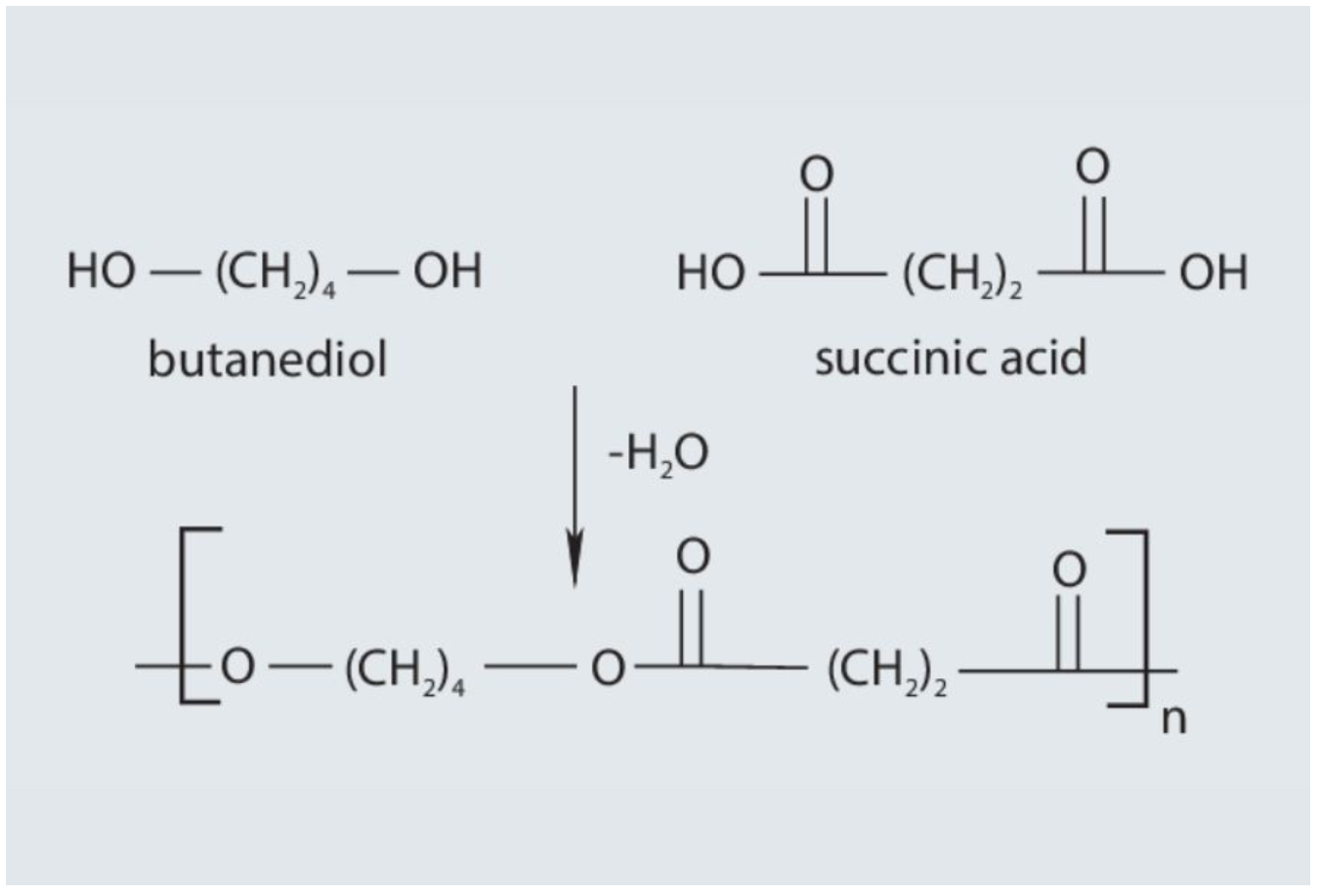
It is a class of biodegradable aliphatic polyesters made from succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol. Compared with traditional petroleum-based plastics and its compostability in compliance with ISO EN13432 standards, the biodegradability of PBS significantly reduces environmental pollution problems, making it one of the key materials for sustainable development.

(pics from wiki.)
2. Material properties of PBS
2.1 Basic properties
①High tensile strength, compressive strength and hardness, comparable to some synthetic plastics. The elongation at break is about 300%.
②The glass transition temperature of PBS is around -30°C, indicating that it still maintains good toughness in low temperature environments.
③PBS has a low moisture absorption rate, which gives it better moisture resistance and enables it to maintain stability in humid environments.
④Its melting point is between 115-120°C, with good thermal stability and high temperature resistance. The melting temperature is lower, which makes PBS less energy-intensive to process.
⑤The crystallinity of PBS is about 40%~60%.
⑥Can be completely biodegraded by microorganisms in the natural environment, leaving no harmful residues.
⑦Anti-UV function protects the product from the harmful effects of sunlight.
2.2 Characteristics
2.2.1 Good processing performance
It can be used for various types of molding processing on general-purpose processing equipment. It has the best processing performance among general-purpose degradable plastics at present. Almost all molding and processing methods used in current resin materials (blow molding, injection molding, extrusion molding, sheet molding, foam molding, vacuum molding, etc.) can be applied to the processing of PBS.
2.2.2 Degradability
①What is degradability?
It refers to its ability to decompose plastic into carbon dioxide and water through the action of enzymes and naturally occurring microorganisms after it is discarded.
②PBS controlled biodegradation is divided into three stages:
Slow phase - Acceleration Phase 2 - Stationary phase.
The efficiency of biodegradation is affected by the size and shape of the material. Compared to granules, PBS powder or film degrades better because of its larger available surface area.
2.3 Synthesis method
2.3.1 Chemical synthesis method
Specific steps:
①Raw material preparation: The synthetic raw materials of PBS include butanediol (BDO) and succinic acid (SA). These chemicals are carefully purified to ensure smooth progress of the reaction.
②Condensation polymerization reaction: The synthesis of PBS is mainly achieved through condensation polymerization reaction. This process generally uses the melt polycondensation method, where butanediol and succinic acid are reacted at high temperature under the action of a catalyst. Moisture is removed during the reaction to promote the polymerization reaction.
③Post-processing: The synthesized PBS needs to undergo post-processing steps such as cooling, cutting and drying to obtain particles or sheets suitable for industrial applications.
2.3.2 Biosynthesis method
Microbial fermentation technology allows microorganisms to be modified to produce PBS. The advantage of this method is that it can effectively utilize renewable resources and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. The specific process includes:
① Strain culture: Select a suitable microbial strain for culture to improve its efficiency in producing PBS.
② Fermentation production: Place the cultured microorganisms in a fermentation tank, and adjust the culture conditions (such as temperature, pH, oxygen supply, etc.) to make the microorganisms produce PBS.
③Separation and purification: After the fermentation is completed, the PBS needs to be separated and purified to obtain a high-purity PBS product.
2.4 Use PBS to synthesize other materials
Materials synthesized using PBS are also called bio-based composites, in which biodegradable natural fibers are combined with a biodegradable or non-biodegradable polymer matrix.
Among the list of aliphatic polyesters, PBS is a promising alternative for producing high-performance, environmentally friendly, biodegradable plastic materials. PBS has excellent processing properties in areas such as textiles and injection molding, making it a highly versatile polymer.
3. Application areas
3.1 Packaging materials
Includes disposable cutlery, shopping bags and food packaging. Its biodegradability allows these application products to degrade naturally after use, reducing the burden on the environment.

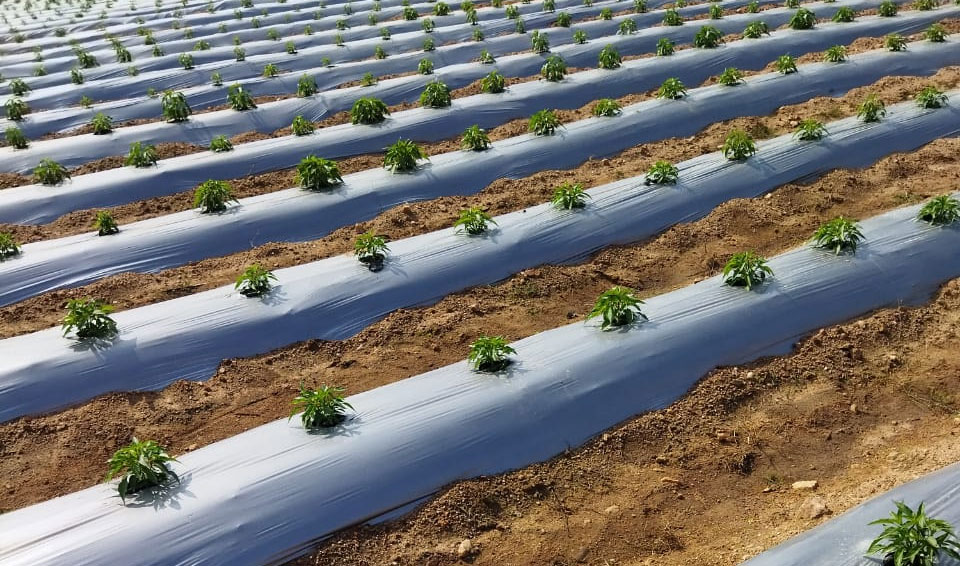
3.2 Agricultural film
Such as mulching films, these films can naturally degrade after use in farmland, effectively reducing soil pollution. In addition, PBS also plays a role in textiles and is used to make biodegradable fibers to meet the needs of green textiles.

3.3 Medical field
①Syringes: Used to manufacture syringes to minimize the risk of infection.
②Catheters: Used to produce catheters that deliver drugs or liquids into the body.
③Wound dressing: used to make wound dressing pads to provide protection for wounds.
4. Market prospects
4.1 Market overview
According to the 2019 global bioplastics production capacity of the European Bioplastics Association, among biodegradable plastics, PBS production capacity is a material after PBAT.

Industrially, improvements in the synthesis of PBS allowed large-scale production of this polymer. Japan's Showa Polymer Corporation built a semi-commercial plant in 1993 with a capacity to produce 3,000 tons of polymer per year. Sold under the tradename Bionolle, these polyesters are synthesized by melt polycondensation followed by chain extension with diisocyanates. In April 2003, Mitsubishi Chemical built a production capacity of 3,000 tons/year and launched PBS called GS Pla (green sustainable plastic) to the market. The polymer's high molar mass eliminates the need for chain extenders.
In the Chinese market, several PBS manufacturers have emerged, such as Hexing Chemical (Anhui, China) and Xinfu Pharmaceutical (Hangzhou, China). In 2010, Hexing Chemical became China's first large-scale PBS company, with an annual production capacity of 10,000 tons. In the same year, Xinfu Pharmaceutical announced the completion of the world's largest continuous PBS production line with an annual output of 20,000 tons. Hangzhou Xinfu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shandong Fuwin New Material Co., Ltd. and Shanxi Jinhui Zhaolong New Material Technology Co., Ltd. realized PBS industrialization in 2008, 2010 and 2012 respectively, building a total of 75,000 tons/year. Production equipment, total output exceeds 50% of the world's, and related products have passed certification in major markets around the world.
Currently, most polyalkylene succinates are synthesized from petrochemical precursors. Nonetheless, most manufacturers are evaluating or developing biobased succinic acid for the synthesis of these polyesters. In 2016, Showa Denko announced the termination of production and sales of Bionolle, citing delays in the penetration of environmental regulations for plastic shopping bags and falling market prices for biodegradable plastics.
In recent years, the PBS material market has also attracted attention from PTT MCC Biochem Company Limited, a joint venture between Mitsubishi Chemical and Thailand's PTT Global Chemical. The product is called BioPBS™. The current PBS production capacity is 20,000 tons/year and is expected to be in 2025. The annual production capacity can reach 40,000 tons/year. China's Blueridge Tunhe's PBS production capacity can reach 120,000 tons/year. Due to low market demand, the current production capacity is 30,000 tons/year; Kingfa Technology PBS has a small amount of production, and based on customer demand, it is expected to expand production next year; Yingkou Kanghui Petrochemical's PBS project with an annual output of 33,000 tons/year is under construction and is expected to be put into operation by the end of the year; Jinhui Zhaolong's PBS is currently in the final trial stage. Inner Mongolia Dongyuan Technology Co., Ltd. plans to build a PBS biodegradable polyester project with an annual output of 200,000 tons in Wuda Industrial Park, Wuhai Economic Development Zone.
4.2 Prospects and challenges
Prospects: As a biodegradable material, PBS is widely optimistic about its market prospects. Due to the global emphasis on environmental protection and sustainable development, the demand for PBS is expected to gradually increase. Especially in the packaging and agricultural sectors, its excellent biodegradability properties make it an ideal choice.
Challenge: The current production cost of PBS is relatively high, which is mainly due to the price of raw materials and the complexity of the production process. Although the degradation rate of PBS is relatively fast, it may still take a long time under certain environmental conditions, which places higher requirements on its performance in certain applications. The production process of PBS requires more resources and energy. Therefore, how to improve production efficiency and reduce costs is still the focus of research.
The video version of this article:
Disclaimer
1. The above remarks only represent the author’s own opinions and do not represent the position of this site;
2. When reprinting articles, please indicate that they are from "Plas.com (www.plas.com)" and include the author’s name. Commercial use requires authorization from the author and the website;
3. If there is any infringement, please contact the author directly, or send a written letter to our company for transmission and processing;
Latest News

Samyang Corporation launches flame-retardant polycarbonate, proving no harmful per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds detected

Seven European companies jointly create 100% recyclable wind turbine blades

Thai fast-selling household brand Vixol launches recycled HDPE bottles
Contact Us
Get App
Top